Where do I find my WEP, WPA, or WPA2 key?
If you are using a router that provides Wi-Fi Internet connections, you need a password to authenticate a connection to the network. If you don't know the password, but you own or administer the router yourself, view the password or reset it to something new using the steps below.
First, let's briefly discuss how Wi-Fi passwords work so you can better understand how they're configured.
Wireless encryption methods
The three types of authentication for consumer Wi-Fi are WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), WPA and WPA2. Most home routers have all three options, but WPA2 is the most secure and should always be used if possible.
- WEP stands for Wireless Equivalent Privacy and was introduced in September 1999, and originally provided only 64-bit encryption (it was later upgraded to offer 128-bit encryption). WEP was officially deprecated in 2004 because it is less secure than the newer methods. However, it is still found on modern routers for purposes of backward compatibility.
- WPA stands for Wi-Fi Protected Access. Introduced in 2003, it supports 256-bit encryption methods including AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). It was intended to bridge the gap between WEP and the more complex WPA2.
- WPA2 is an updated version of WPA which was introduced in 2004. It enforces AES and implements some stronger supporting protocols such as CCMP (Counter Cipher Mode). While WPA2 still has some known vulnerabilities, they require significant computing resources, and the attacker must already be able to access the local wireless network. WPA2 is still used today as the standard for robust consumer-level wireless encryption.
Most routers offer two types of WPA2 encryption, called WPA2-Personal and WPA2-Enterprise. The enterprise version of WPA2 is for corporate settings where an IT department controls company-wide security policies. For other settings, including wireless Internet in your home, WPA2-Personal is the encryption method to use.
All these methods require a password, also known as an encryption key when you try to connect. If you provide the correct key, a wireless connection is established.
I don't know what my key is. How do I connect to the wireless network?
If you forgot the key for connecting to your wireless network, you must access the router's configuration interface using an Internet browser.
Normally, you could do this over the wireless network. But because you don't have the password, you cannot.
Therefore, to connect to the router, you have two options:
Create a wired connection to the router

If you have an Ethernet cable, and an Ethernet port on your computer, you can create a wired connection to your router.
Routers sometimes come packaged with a short Ethernet cable, also known as a category 5 cable, for exactly this purpose. It should have a connection at each end like the one pictured at right. If you don't have one, you can purchase one online, or at your local electronics store. A short cable length is fine — 3-feet should be sufficient.

Connect one end of the cable to your computer or laptop. Connect the other end to the back of the router, as shown in the picture.
Your router may have one Ethernet port for incoming connections, labeled "WAN" that is for the Internet connection. Do not connect your Ethernet cable to this port. Instead, connect your cable to one of the ports marked "LAN." These ports distribute the Internet to other devices, such as your computer.
After connecting the cable to both your computer and your router, your operating system should automatically detect the connection. You can now proceed to access your router's configuration.
Reset the router to its factory defaults
If you don't have an Ethernet cable, or if making a wired connection is otherwise inconvenient, you can reset your router to the factory default settings. Doing so resets the name of your wireless network also known as the SSID (service set identifier) and the encryption key. These default values are often found printed on a sticker affixed to the case of the router itself.
If you decide to factory reset your router, be aware that any other custom configuration or other changes are going to be reset to the default settings. Check the manufacturer's documentation for your model of router before proceeding. If you don't have the physical instruction manual, you can find it online under the "support" section of your manufacturer's website.
After resetting your router to factory defaults, you'll be able to connect to the wireless network using the default SSID and encryption key. When you are connected, you can proceed to the next step, accessing your router's configuration.
For more information about resetting your router, see: How to reset a forgotten username and password on a router.
Accessing the router configuration
Once you have connected to your wireless router (by a wired connection, or using the default wireless network credentials), you can access your router's configuration in a web browser. In a browser window, enter your router's IP address in your browser's address bar, and press Enter.
If you're unsure what your router's IP address is, you can try one of these common router addresses:
- 192.168.0.1
- 192.168.1.1
- 10.0.0.1
- 10.0.1.1
Some routers also allow you to connect by entering a hard-coded URL (uniform resource locator). For instance, many Netgear wireless routers allow you to use the address www.routerlogin.net to access your router.
Consult your router's manual for the correct address of your router, and navigate to that address in your web browser.
Logging into the router as an administrator
After navigating to your router's IP address in your web browser a login prompt should appear asking your for the router's administrator username and password.
If you don't remember the administrator name and password, or if you're unsure, consult your router's manual for the default login values. Below are commonly used insecure defaults.
- admin / admin
- admin / password
Never leave your router's administrator name and password at their default values as they anyone can find them via an Internet search. Always change these values when configuring your wireless router. At a minimum, change the password to a strong password you'll remember.
If you cannot log into your router because you can't remember the login information, and the default username and password don't work, you can reset the router to factory defaults.
Once you have logged in, you can view or change your router's configuration.
Viewing and changing the encryption key (wireless password)
Every router's configuration interface is different. Below is an example of how a router's setup may appear.
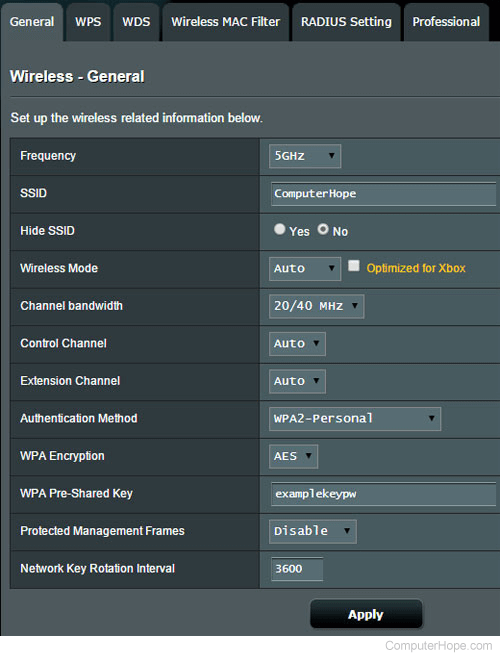
In your router's configuration interface, look for a section called Wireless, or something similar. You're looking for the page where you can change the wireless network's configuration, including its SSID name and authentication key. If you're unable to locate it, consult your router's manual for specific instructions.
When you find the wireless network configuration page, you can view the values and make changes. For Authentication Method, choose WPA2-Personal. You can set the encryption key (password) in one of the text fields below this. Consult your manual if you're unable to locate the correct field.
The encryption key is often displayed in plain text, so if you only need the current password, it should be visible on this page.
At this time, change your SSID name, which is the name that appears in the list of available wireless networks.
If you make any changes to your router's configuration, make sure to save them. For instance, in the example pictured above, you'd click the Apply button.
Many modern wireless routers offer two wireless networks which broadcast at frequencies of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, respectively. The configuration for each network may appear on separate pages. If you are using both networks, make sure they are both configured the way you want, and you know the password for each. Consult your router's manual for more information regarding dual-band Wi-Fi configuration.
Verify you can connect to the wireless network
- Make sure all changes are saved and you have restarted your router, if necessary. If you are using a wired connection, disconnect the Ethernet cable now.
- If you changed the SSID or key, you are disconnected from your router when the new configuration takes effect. Therefore, you'll need to log into your wireless network using the new credentials.
- If you reset your router to its factory defaults, we recommend you change the router's administrator username and password to something other than the default values. You can do this from in the router's configuration interface. Consult your router's manual if you have any difficulty locating the correct menu and configuration options.
If you've tried all the above suggestions and still can't log on, we recommend contacting the router manufacturer directly for technical support.
