Signal
A signal may refer to any of the following:
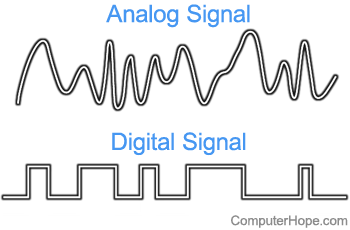
1. In electronics, a signal is an electrical pulse that's used as a method of transmitting data. A connection is established when a signal is successfully received, and the receiving device interprets the signal's data. For example, when your TV has a picture, it's receiving a signal. If no signal is received or its data is not understood, the TV may show static or a no signal error message.
Examples of signals include an analog signal and digital signal. As seen in the picture, an analog signal is made of waves and can represent a frequency with many different values. A digital signal operates more like binary and has either an off or on value.
2. Signal is a secure messaging application developed by Open Whisper Systems for iOS and Android, with desktop versions available for Linux, Windows, and macOS. It encrypts data transfers such as text messages, images, video, and voice calls, with one or multiple recipients. It uses end-to-end encryption, enabling users to communicate with maximum privacy. A mobile phone number is required to register for a Signal account, even for the desktop application.
The Signal server and client are open-source, which allows anyone to scrutinize their code for weaknesses or vulnerabilities. More information and downloads are available on the official Signal website, and the Signal source code is available on the Signal app GitHub page.
3. Signals are software interrupts for interprocess communication in Unix and Unix-like operating systems such as Linux. See our Linux signals guide for further information on signals.
Data signal, Digital signal, Electronics terms, Modulate, PM, Pulse, Relay, Repeater
