Current directory
Alternatively called a working directory or CWD (current working directory), the current directory is the directory or folder where you are working. The following sections contain some common use examples involving the current working directory.
Windows current directory
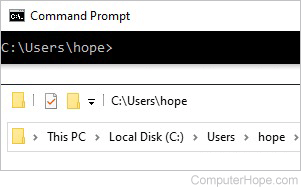
While in Windows Explorer, the current working directory is shown at the top of the Explorer window in a file address bar. For example, if you were in the System32 folder, you would see "C:\Windows\System32" or "Computer > C:>Windows\System32" depending on your version of Windows. In this example, System32 is the current directory.
In Windows, a directory is more properly called a folder, not a directory.
MS-DOS and Windows command line current directory
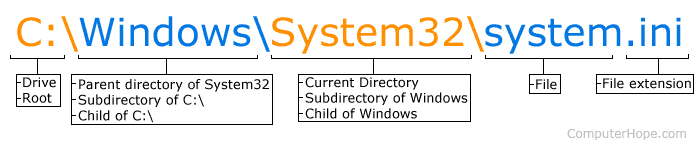
In the MS-DOS or Windows command line, the current working directory is displayed as the prompt. For example, if the prompt was "C:\Windows\System32>" the "System32" directory is the current directory, "Windows" is the parent directory, and "C:\" is the drive (root directory). To list the files in the current directory, use the dir command, and to change the current directory, use the cd command.
You can use the chdir command by itself to print the current directory in MS-DOS and the Windows command line.
Show the current directory in Linux and Unix
Depending on your Linux or Unix variant and its shell, the current directory may be shown as the prompt or when using the pwd (print working directory) command.
How to list files in the current directory
To list the files and directories in the current directory depends on your operating system. If you're using Microsoft Windows or MS-DOS, you can use the dir command to list the files and directories in the current directory. If you're using Linux, you can use the ls command to list the files and directories in the current directory.
Linux, MRUD, Operating system terms, Parent directory, Root directory, Unix, WD
