Msconfig
Msconfig, also known as the System Configuration Utility, is a Microsoft utility introduced with Windows 98 and available in all later versions of Windows. It is used to configure how a computer starts and what programs and services load when Windows starts. Users running Windows 98 or later versions can open msconfig by following the steps below.
How to open msconfig
Users running Microsoft Windows XP and later need to have administrator rights to run msconfig. This utility is not available in Windows 95, Windows NT, or Windows 2000.
Windows 11
- On the Windows taskbar, click the magnifying glass icon.

- In the text field at the top of the search window, type msconfig and press Enter.
- The System Configuration Utility window should open, as shown in the example pictures and overview.
Windows 10
- On the Windows desktop, type msconfig in the "Search the web and Windows" text box next to the Start menu button on the taskbar.
- Select the System Configuration option in the search results or press Enter.
- The System Configuration Utility window should open, as shown in the example pictures and overview.
Windows 8
- Open the Windows Start Screen.
- Type msconfig and press Enter.
- The System Configuration Utility window should open, as shown in the example pictures and overview.
Windows Vista and Windows 7
- Open the Start menu.
- In the Search programs and files text box, type msconfig and press Enter.
- The System Configuration Utility window should open, as shown in the example pictures and overview. If the UAC (User Account Control) prompts you for permission, click the Continue button.
Windows 98 and Windows XP
- Open the Start menu and select the Run option.
- Type msconfig and press Enter.
- The System Configuration Utility window should open, as shown in the example pictures and overview.
Windows msconfig example pictures and overview
After running the msconfig command, a System Configuration window should open, similar to what is shown in the picture below.
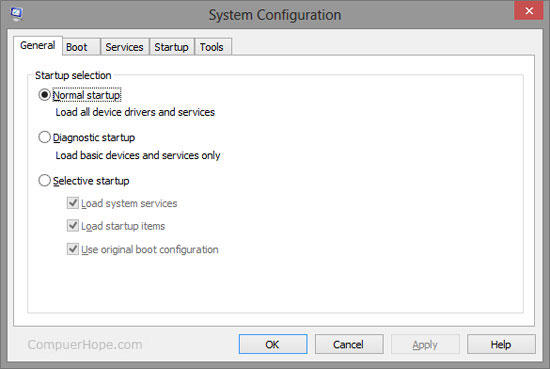
Click any of the links below for additional information and examples about each of the available options.
General tab

The General tab is the default tab in the System configuration and shows how the computer starts. By default, Normal startup should be selected. If you've changed any of the settings in the Boot tab or disabled any programs or services from starting up, the Selective startup will be selected. When the operating system uses Selective Startup, it gives you a reminder notification that Selective Startup is being used.
Earlier versions of Windows, such as Windows XP, also included two buttons that were later removed. These two buttons were the "Launch System Restore" button, which opened the Windows System Restore feature, and the "Expand File" button, which allowed the user to expand any compressed file.
Boot tab
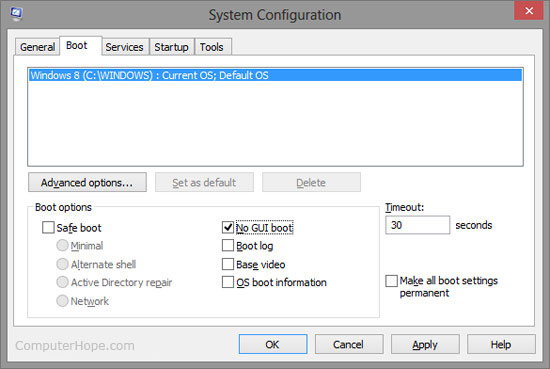
The Boot tab is an option added later into the System Configuration utility (Windows 98 and XP have boot.ini). This tab lets you make the same adjustments you can make in the Windows boot.ini file without editing the file. You can adjust additional settings in Advanced options, such as the number of processors to use during boot, maximum memory, and other debug options.
Services tab
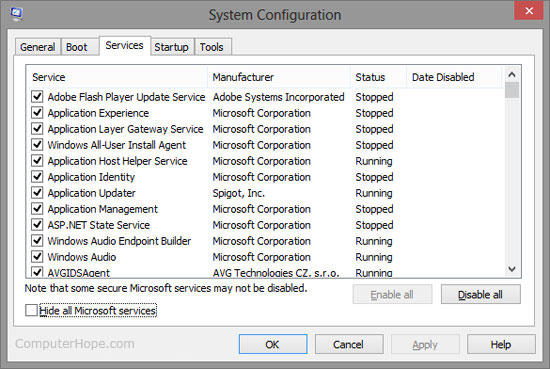
The Services tab lets you enable or disable any Microsoft Windows services or other program services you have running on the computer. Check the "Hide all Microsoft services" box at the bottom of the window to only see non-Windows services such as driver services and program services. Unchecking a box disables the service from starting.
Startup tab
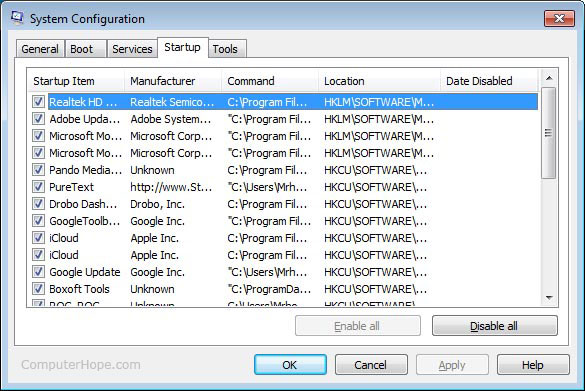
The Startup tab is one of the most frequent reasons most Windows users enter the System Configuration utility. In the Startup tab, you'll be able to start and stop any of the programs (TSRs) that open each time your computer starts. These startup programs are often one of the biggest causes for a computer to startup and run slow. Uncheck any program that you want to disable from starting up each time.
In Windows 8, Microsoft has removed this feature in the System Configuration utility and moved it into the Windows 8 Task Manager.
Tools tab
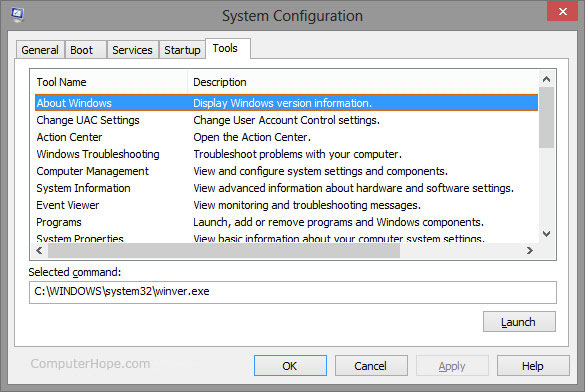
The Tools tab gives you quick access to all the Microsoft Windows tools. For example, you can access the Event Viewer tool by selecting the Event Viewer option in the tool name list and clicking the Launch button.
SYSTEM.INI
The SYSTEM.INI tab gives Windows 98 and Windows XP users quick access to editing and enabling and disabling the Windows system.ini file.
WIN.INI
The WIN.INI tab gives Windows 98 and Windows XP users quick access to editing and enabling and disabling the Windows win.ini file.
BOOT.INI
The BOOT.INI tab gives Windows 98 and Windows XP users quick access to editing and enabling and disabling the Windows boot.ini file.
Msinfo32, Operating system terms, Startup, Sysedit, Windows Accessories
