Schema

A schema may refer to any of the following:
1. In general, a schema refers to any plan or vision that is a well-thought-out document with set rules and restrictions.
2. With a database, a schema describes the structure and rules of a database and the relationships of data elements.
Example database schema
Here is a simple, non-scaling schema for users and their read/write permissions. It has three tables (tblUsers, tblPermissions, and tblUsersPermissions), with only a few columns in each. It defines two relationships (one-to-many from tblUsers to tblUsersPermissions, and one-to-many from tblPermissions to tblUsersPermissions), commonly shown in an ERD (entity relationship diagram) as 1 -> ∞.
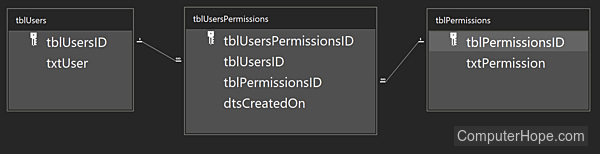
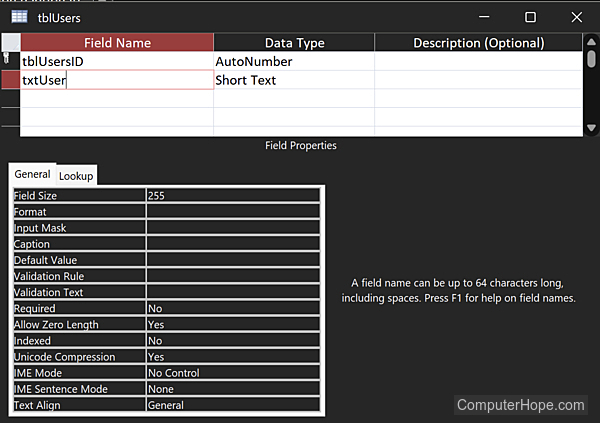
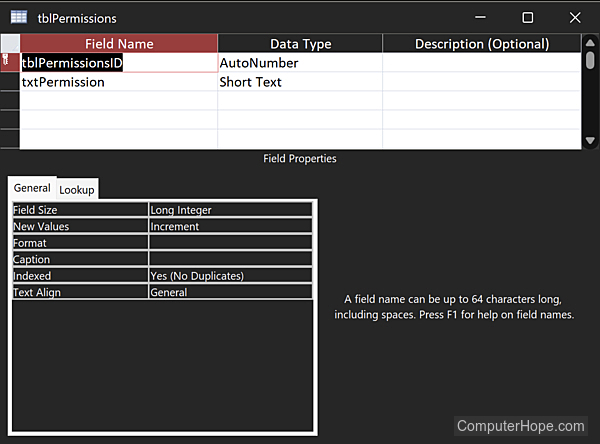
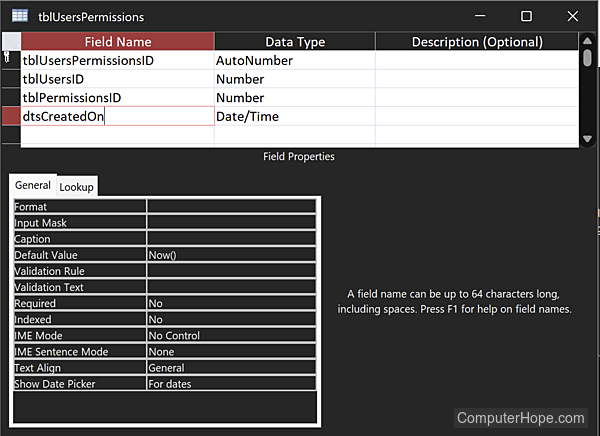
Using this database schema, data can be added to a database.
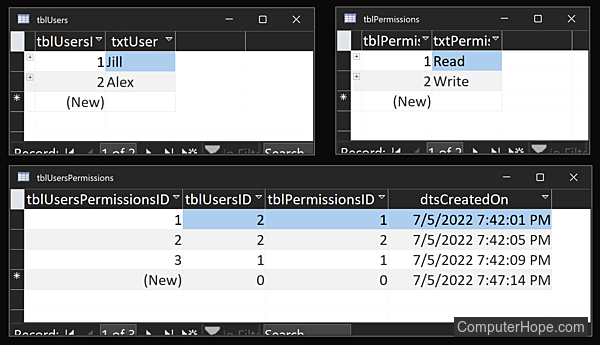
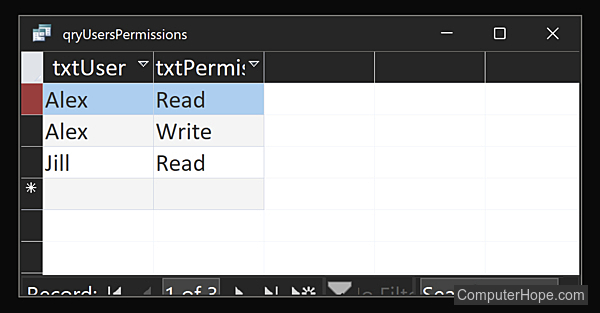
Using SQL (Structured Query Language), you can retrieve a list of users and their permissions.
SELECT tblUsers.txtUser, tblPermissions.txtPermission FROM tblUsers INNER JOIN tblUsersPermissions ON tblUsers.tblUsersID = tblUsersPermissions.tblUsersID INNER JOIN tblPermissions ON tblUsersPermissions.tblPermissionsID = tblPermissions.tblPermissionsID ORDER BY tblUsers.txtUser, tblPermissions.txtPermission;
3. With an API (application programming interface), a schema formally defines how data is properly transmitted to an API. It also dictates how the API responds to the request.
