Linux who command

On Unix-like operating systems, the who command displays users logged in to the system.
This page covers the GNU/Linux version of who.
Description
The who command prints information about all users who are currently logged in.
Syntax
who [ OPTION ]... [ FILE ] [ am i ]
Options
| -a, --all | Same as using the options -b -d --login -p -r -t -T -u. |
| -b, --boot | Display the time of the last system boot. |
| -d, --dead | Display dead processes. |
| -H, --heading | Print a line of column headings. |
| --ips | Print IP addresses instead of hostnames. With --lookup, canonicalizes based on stored IP, if available, rather than stored hostname. |
| -l, --login | Print system login processes. |
| --lookup | Attempt to canonicalize hostnames via DNS (domain name system). |
| -m | Only print information about the user and host associated with standard input (the terminal where the command was issued). This method adheres to the POSIX (portable operating system interface for Unix) standard. |
| -p, --process | Print active processes spawned by init. |
| -q, --count | Displays all login names, and a count of all logged-on users. |
| -r, --runlevel | Print the current runlevel. |
| -s, --short | Print only name, line, and time fields, which is the default. |
| -t, --time | Print the last time the system clock was changed, if the information is available. |
| -T, -w, --mesg | Add a character which indicates the state of the terminal line: "+" if the terminal is writable, "-" if it's not, or "?" if a bad line is encountered. |
| -u, --users | Print the idle time for each user, and the process ID. |
| --message | Same as -T. |
| --writable | Same as -T. |
| --help | Display a help message, and exit. |
| --version | Display version information, and exit. |
Notes
If FILE is specified, who gathers its information from this file. Otherwise, it reads from a default file location (usually /var/run/utmp).
If the arguments "am i" are specified, who assumes the -m option.
Examples
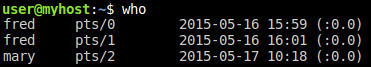
who
Displays the username, line, and time of all currently logged-in sessions. For example:
who am i
Displays the same information, but only for the terminal session where the command was issued, for example:
alan pts/3 2013-12-25 08:52 (:0.0)
who -aH
Displays "all" information, and headers above each column of data, for example:
NAME LINE TIME IDLE PID COMMENT EXIT
2014-01-17 07:00 154 id=si term=0 exit=0
system boot 2014-01-17 07:00
run-level 2 2014-01-17 07:00 last=S
2014-01-17 07:01 1607 id=l2 term=0 exit=0
LOGIN tty6 2014-01-17 07:01 2809 id=6
LOGIN tty5 2014-01-17 07:01 2808 id=5
LOGIN tty4 2014-01-17 07:01 2807 id=4
LOGIN tty2 2014-01-17 07:01 2805 id=2
LOGIN tty1 2014-01-17 07:01 2804 id=1
LOGIN tty3 2014-01-17 07:01 2806 id=3
pts/0 2014-01-17 11:31 2811 id=ts/0 term=0 exit=0
lucy + pts/1 2014-01-17 22:42 . 6609 (:0.0)
pts/2 2014-01-18 02:14 0 id=/2 term=0 exit=0
pts/3 2014-01-18 02:08 0 id=/3 term=0 exit=0
pts/4 2014-01-17 21:30 0 id=/4 term=0 exit=0
lucy + pts/0 2014-01-17 22:01 01:04 6330 (:0.0)
Related commands
date — Output the current date and time.
last — Display a listing of the most recently logged-in users.
login — Begin a session on a system.
mesg — Control if (non-root) users can send messages to your terminal.
su — Become the superuser or another user.
w — Show who is logged on and what they are doing.
whoami — Print your effective userid.
