CD-ROM

Short for Compact Disc Read-Only Memory, a CD-ROM is an optical disc containing audio or software data whose memory is read-only. A CD-ROM Drive or optical drive is the device used to read them. CD-ROM drives have speeds ranging from 1x to 72x, meaning it reads the CD (Compact Disc) roughly 72 times faster than the 1x version. As you would imagine, these drives can play audio CDs and read data CDs, including CD-R (Compact Disc Recordable) and CD-RW (Compact Disc Re-Writable) discs.
A CD-ROM drive cannot read a DVD (Digital Versatile Disc), including movie DVDs and data DVDs. The DVD format is different than a CD, and a CD-ROM drive is not designed to read the format of a DVD. A DVD-ROM (Digital Versatile Disc Read-Only Memory) drive or later disc technologies like Blu-ray drive is required to read a DVD.
CD-ROM was featured as a top term of 1994.
Does my computer have a CD drive?
Today's newer computers no longer have disc drives (CD drive). To determine if your computer has a CD drive, examine the front of the computer. The front of the computer should have a slot or tray that opens to read a CD. If you visually cannot see a CD drive, browse your computer drives to see if your operating system lists a disc drive.
If you see no disc drive, your computer doesn't have a CD drive. However, a CD drive can be installed into a desktop computer, or an external CD drive can connect to a desktop or laptop.
Disc drive overview
Below is a picture of the front and back of a standard IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) CD-RW disc drive from Memorex.

How to open and close a CD-ROM drive

A CD-ROM drive can be opened by pressing the tray eject button on the front of the drive (pictured right). To close the CD-ROM drive, press the tray or the eject button again.
With some computer cases, the eject button may be hidden behind the case to make the case look more visually appealing. If you don't see an eject button, try pressing on the right side of the disc drive, which is often toward the top of the tower.
If the eject button is not working, you can open or eject the tray through My Computer, or "This PC" in newer versions of Windows. In My Computer, find the list of drives in the computer, then right-click the CD-ROM drive and select Eject in the pop-up menu.
A CD-ROM drive can also be manually opened by inserting the end of the paperclip into the drive eject hole. Insert it gently until you feel resistance, then press in a little further to activate the release mechanism. If done properly, the tray should open a little bit, and you can use your fingers to pull the tray out gently. Manually opening or ejecting the tray can be useful for removing a CD that is stuck in the CD-ROM drive.
Which drive letter is the CD-ROM?
By default, your CD-ROM should be designated by D: when you are viewing the various drives on your computer. However, when adding a new hard drive or partition, a CD-ROM's drive letter may be moved further down the alphabet (e.g., from D: to E:). To be sure which drive letter your CD-ROM is under, follow the steps below.
- Open Windows Explorer by pressing the Windows key+E.
- From the list on the left side of the Explorer window, click This PC.
- You should see a list of all your computer's drives and their respective letters, as shown below.
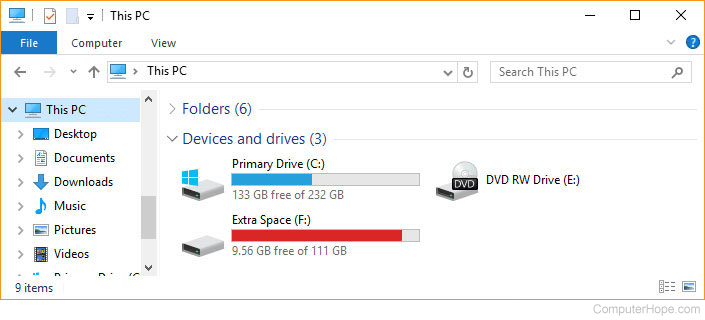
If there is a CD, DVD, or another disc in the disc drive you wanted to run double-click the disc drive icon in Explorer. If the disc AutoPlays and you want to browse the files on the disc, right-click the disc icon and choose Open or Explore.
CD-ROM and disc drive interfaces
Below are the different interfaces that allow a CD-ROM and other disc drives to connect to a computer.
- IDE/ATA - One of the most commonly used interfaces for disc drives.
- Panasonic - Older proprietary interface.
- Parallel - Interface used with old external CD-ROM drives.
- PCMCIA (PC Card) - Interface sometimes used to connect external disc drives to laptop computers.
- SATA (Serial AT Attachment) - Replacing IDE as the new standard to connect disc drives.
- SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) - Another common interface used with disk and disc drives.
- USB (Universal Serial Bus) - Interface most commonly used to connect external disc drives.
CD-ROM transfer speeds
Below are the standard transfer rates and access times for CD-ROM drives. The below figures are averages you can expect to find on each speed of CD-ROM drive.
| Drive speed | Transfer rate (Mbit/s) | Access time (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| Single speed (1x) | 1.2288 | 400 |
| Double speed (2x) | 2.4576 | 300 |
| Quad speed (4x) | 4.9152 | 150 |
| Six speed (6x) | 7.0653 | 150 |
| Eight speed (8x) | 9.8304 | 100 |
| Ten speed (10x) | 12.288 | 100 |
| Twelve speed (12x) | 14.7456 | 100 |
| Eighteen speed (18x) | 21.8343 | 90 |
| Twenty speed (20x) | up to 24.576 | 90 |
| Thirty-two speed (32x) | up to 39.3216 | 85 |
| Thirty-six speed (36x) | up to 44.2368 | 80 |
| Fifty-two speed (52x) | up to 63.8976 | 80 |
| Seventy-two speed (72x) | up to 88.4736 | 75 |
| CAV (Constant Angular Velocity) drives (12x - 24x) | 1,843,200 - 3,686,400 | 150-90 |
History of the CD-ROM
The compact disc was developed by Philips and Sony in 1982. Denon expanded on the CD-DA (compact disc digital audio) format to create the CD-ROM format, allowing it to store any data and not only audio.
In 1984, Denon and Sony introduced the CD-ROM format to the public at a Japanese computer show. The first CD-ROM disc introduced to the public had a storage capacity of 553 MB. Today, a standard CD-ROM disc can store up to 700 MB of data, or 80 minutes worth of audio. Non-standard CD-ROM discs also exist that store up to 900 MB of data, or 99 minutes of audio.
Where can I buy a CD-ROM drive or discs?
Below is an affiliate link with Amazon to get a CD-ROM drive or blank discs and support Computer Hope. If Amazon isn't available in your area, we also have a link to other places to buy computer parts.
- Amazon affiliate link for a CD-ROM drive.
- Amazon affiliate link for CD-Rom blank discs.
- Where to buy computer hardware parts.
CD-R, CD-RW, CD terms, Compact disc, Computer acronyms, Disc drive, Drive, Hardware terms, ISO image, Laser, Media, Multimedia, Optical disc, Read-only, Storage device, X
