Measurement
A measurement determines a dimension, capacity, or quantity of an object, or the duration of a task.
In computers, measurements are constantly occurring and determining the computer's function. These measurements include whether a storage medium has enough space to store a file, the CPU's current temperature, and how long the user is idle.
Processor speed measurements
The following measurements are used when measuring the frequency (speed) of a computer CPU (central processing unit) and are related to the computer's clock speed. The following list is of processor speeds from lowest to highest.
Capacity measurements
The following measurements are used when measuring the capacity or storage of a computer device, like a hard disk drive. The following list is of capacity sizes from lowest to highest.
Not all manufacturers and developers list their value using binary, which is base 2. For example, a manufacturer may list a product's capacity as one gigabyte (1,000,000,000 bytes, a metric value) and not 1,073,741,824 bytes (gibibyte). Below, we're showing both links, when applicable.
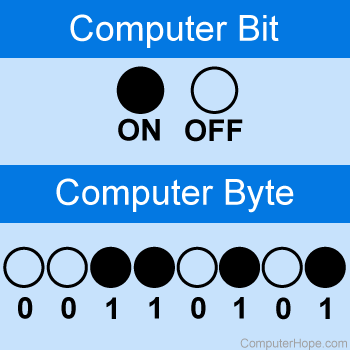
- Bit
- Nibble
- Byte
- Kilobyte (kibibyte)
- Megabyte (mebibyte)
- Gigabyte (gibibyte)
- Terabyte (tebibyte)
- Petabyte (pebibyte)
- Exabyte (exbibyte)
- Zettabyte
- Yottabyte
- Ronnabyte
- Quettabyte
Transmission measurements
Transmission measurements are used when measuring the speed of data transmission. For example, the bandwidth speed of your Internet connection is an example of a transmission speed. The following list is of transmission speeds from lowest to highest.
All computer-related measurements
Below is a listing of the different computer measurements you may encounter while working with a computer or in the computer field.
Absolute unit, Access time, Calibration, Duration, Measure app, Rotational delay, SI, Size
